6 tips to improve your skeletal muscle
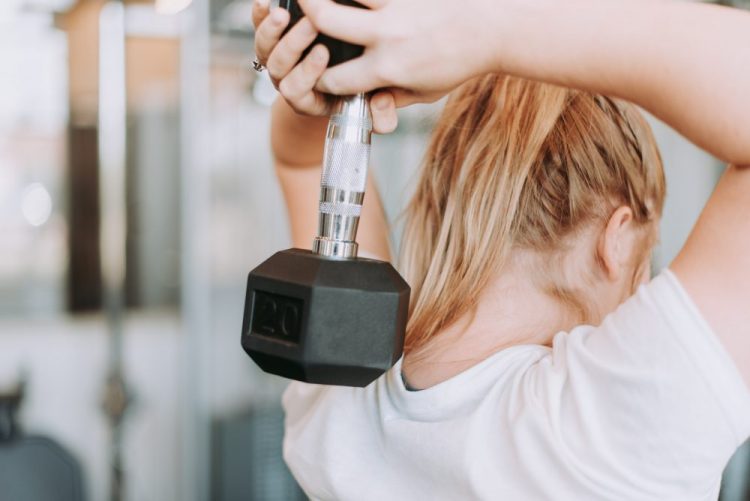


If you are wondering how to build more muscle, or achieve better muscle definition, it is helpful to understand a bit more about muscles in general, and in particular skeletal muscle (also known as striated or voluntary muscle).
Muscle 101
There are 3 main types of muscle tissue in the human body;
- Smooth muscle which supports the internal organs
- Cardiac muscle which enables heart function
- Skeletal muscle
The skeletal muscles in our body are attached to bone and the combination of bones, muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons and nerves enables us to move and control that movement. Most muscle cells develop from a layer of cells which are formed in the womb and are ready to grow and be trained throughout life. Boys and girls have similar amounts of muscle until about the age of 10, after which puberty increases the levels of testosterone in men and drives a much greater expansion of skeletal muscle.
Why are muscles important for health?
As well as controlling movement, muscles play a vital role in supporting overall health and wellness, especially into old age. Muscles store glucose (carbohydrates) and use this as fuel every time you need to move. Muscle mass essentially acts as a reserve that you top up by eating carbohydrates, and deplete when you exercise. A healthy muscle to fat ratio creates a virtuous circle; with a healthy level of skeletal muscle, you are capable of effective movement and exercise; this maintains the muscle and inhibits excess fat storage, which in turn means you are capable of movement and exercise and maintain a healthy level of skeletal muscle! “Muscles store glucose (carbohydrates) and use this as fuel every time you need to move.” Increasing rather than just maintaining your skeletal muscle, and improving the quality of your muscle, will enable you to not just maintain movement and exercise, but to develop and improve it. Of course, we can tell you much more about topics like myoblasts, nuclei, sarcomere and sarcolemma, but we rather keep it less technical and give you some practical tips on how to improve your skeletal muscle.
So, if you are aiming for a PB, how do you improve your skeletal muscle volume and quality?
- Vary your workout - Building muscle means resistance or weight training, not just cardio.
- Follow a healthy diet - Make sure you get enough protein like soya, meat, fish, diary, nuts and pulses etc. to repair the micro-tears in the muscle which occur with resistance exercise.
- Work your biggest muscles - If you’re a beginner, any workout is likely to increase protein storage which enables your muscles to grow. But if you’ve been doing resistance exercise for a while, you’ll build the most muscle if you focus on the large muscle groups, like the chest, back, and legs. And always remember to change your workout routine every 6-8 weeks.
- Plan your rest days - Your muscles grow when you’re resting, not when you’re working out; a challenging weight workout increases protein storage for up to 48 hours, immediately after your exercise session.
- Eat carbohydrates after your workout - Research shows that you’ll rebuild muscle faster on your rest days if you feed your body carbohydrates. Have a banana, a sports drink, or a peanut-butter sandwich.
- Have a glass of milk before bed - Eat a combination of carbohydrates and protein 30 minutes before you go to bed. The calories are more likely to stick with you during sleep and reduce protein breakdown in your muscles.
Finally, monitor your muscle volume, muscle quality and basal metabolic rate to make sure you are consuming the right level of calories to fuel your muscle function, and most importantly to track your progress over time so you can see how well you are doing.
- BC-718Out of stock